Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Lymphoedema is a chronic condition that causes swelling due to fluid buildup, often affecting the arms or legs, but it can occur anywhere in the body. It results from a blocked or damaged lymphatic system, often caused by cancer treatments. In severe cases, it can restrict movement, cause skin infections, and lead to skin damage.
Treatment includes compression bandages, massage, and in some cases, surgery. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Awareness and proper care can help prevent complications like infection and mobility issues.
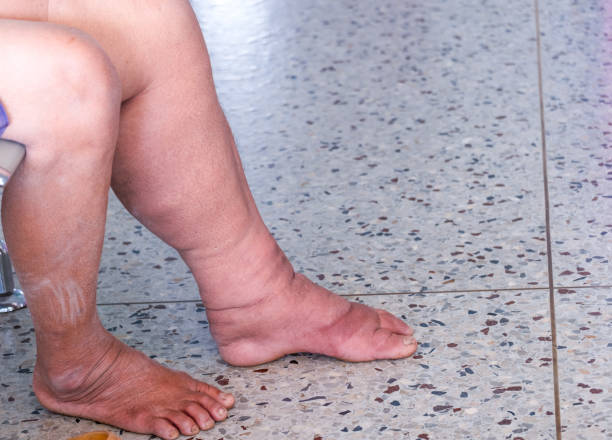
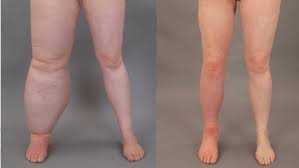
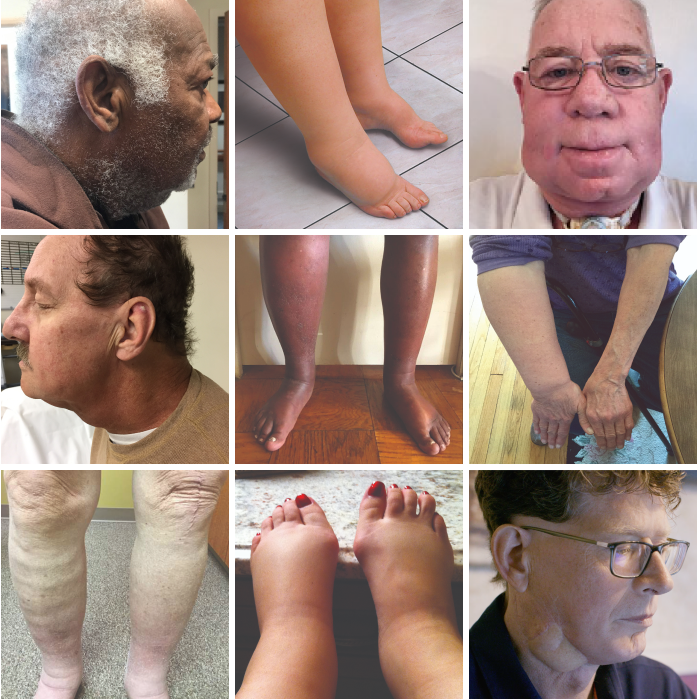
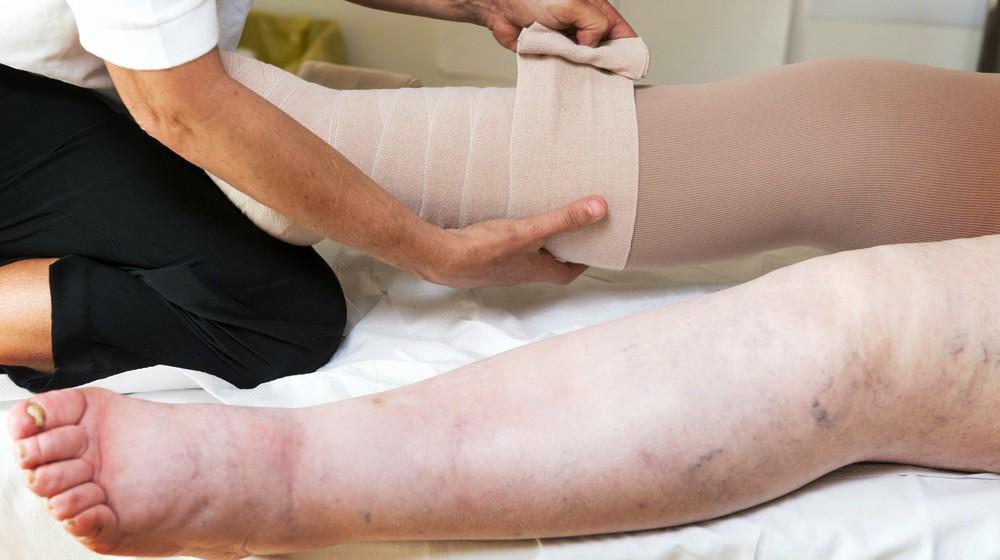
Signs and symptoms
Lymphedema signs and symptoms can range from mild to severe and include:
- Swelling of part or all of the arm or leg, including fingers or toes
- A feeling of heaviness or tightness
- Restricted range of motion
- Recurring infections
- Hardening and thickening of the skin (fibrosis)
Lymphedema caused by cancer treatment may not occur until months or years after treatment.
Causes of Lymphoedema
- Tumors blocking lymph vessels
- Radiation therapy causing scarring
- Surgery removing lymph nodes
- Parasites, especially in tropical regions
Raising awareness about early detection and treatment is essential for managing lymphoedema.
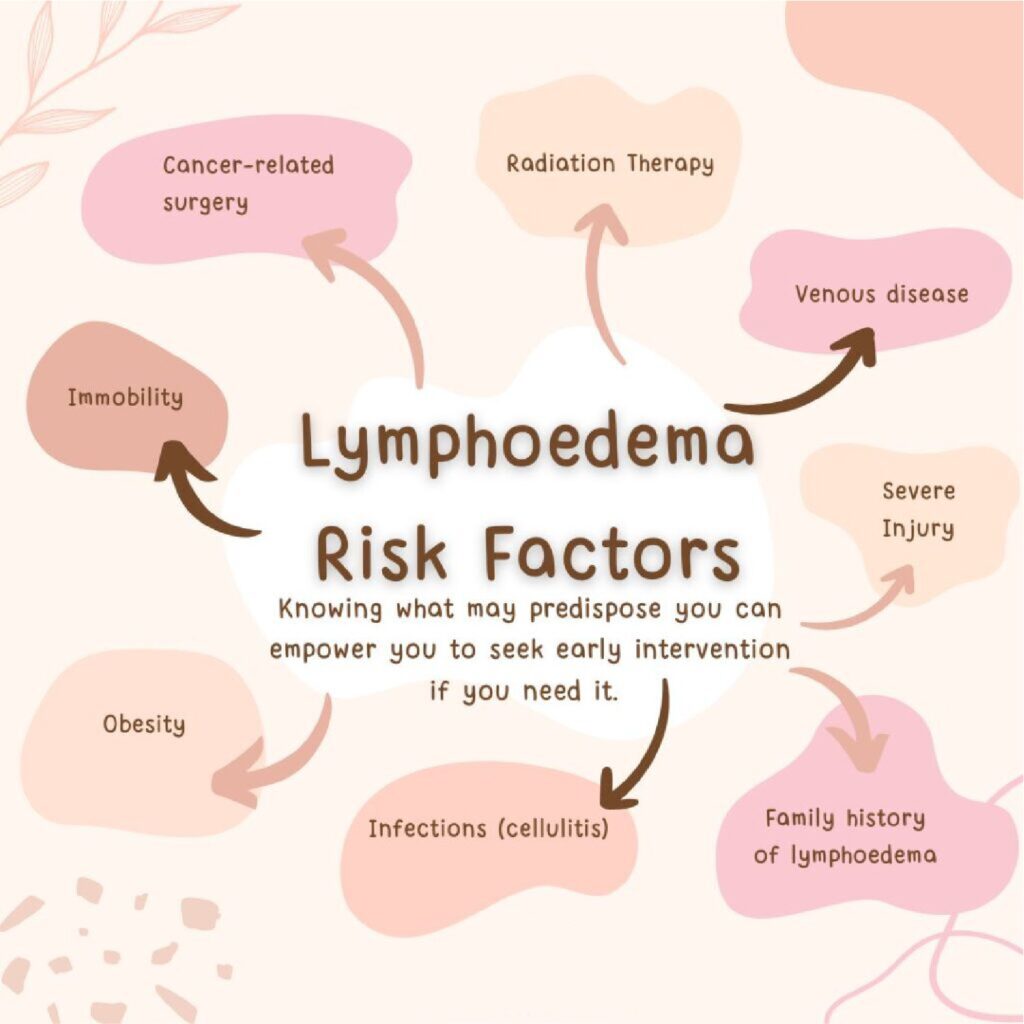
Risk factors of Lymphoedema
Certain factors increase the risk of developing lymphoedema, including:
- Older age
- Excess weight or obesity
- Arthritis (rheumatoid or psoriatic)
- Cancer treatments (surgery and radiation)
- Cancer types such as gynaecological, urological, melanoma, sarcomas, and head and neck cancers
- Immobility and conditions like venous insufficiency, cellulitis, heart or kidney failure, and metabolic disturbances
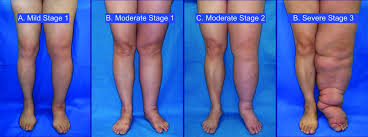
Complications of Lymphoedema
Certain factors increase the risk of developing lymphoedema, including:
- Older age
- Excess weight or obesity
- Arthritis (rheumatoid or psoriatic)
- Cancer treatments (surgery and radiation)
- Cancer types such as gynaecological, urological, melanoma, sarcomas, and head and neck cancers
- Immobility and conditions like venous insufficiency, cellulitis, heart or kidney failure, and metabolic disturbances

Impact of Lymphoedema on Quality of Life
Lymphoedema significantly affects the quality of life for individuals with cancer-related and non-cancer-related forms of the condition. Patients commonly experience disruptions in daily functioning, including:
- Workforce Impact: Many individuals with lymphoedema require extended leave or may face the need to cease employment due to the physical limitations imposed by their condition.
- Infection Recurrence: Repeated cellulitis episodes are common, with some patients experiencing acute flare-ups annually, necessitating intensive medical intervention.
- Hospitalization: Severe cellulitis cases often require admission for intravenous antibiotics, further interrupting daily life and increasing healthcare burdens.
- Chronic Pain: Persistent, uncontrolled pain is a frequent and debilitating symptom, exacerbating the condition’s impact on physical and mental well-being.
Management of Lymphoedema
Effective lymphoedema management begins with early intervention, as timely action can prevent severe swelling and enable patients to better self-manage the condition. Here are core management strategies:
Compression Therapy: Includes compression bandages, specialized garments, and intermittent pneumatic compression devices to reduce and control swelling.
Lymphatic Drainage: Techniques such as Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD), a specialized massage to stimulate lymph flow, and Simple Lymphatic Drainage (SLD), a self-administered massage, can help.
Exercise and Weight Management: Physical activity aids lymphatic drainage and is safe when done with compression garments (except for swimming). Weight management is crucial for patients with high BMI.
Skin Care: Essential to maintain skin integrity and reduce infection risk, which can complicate lymphoedema.
Surgical Options: Emerging surgical options, like lymphatic venous anastomosis (LVA), liposuction, and lymph node transfer, offer additional solutions, though access is limited.

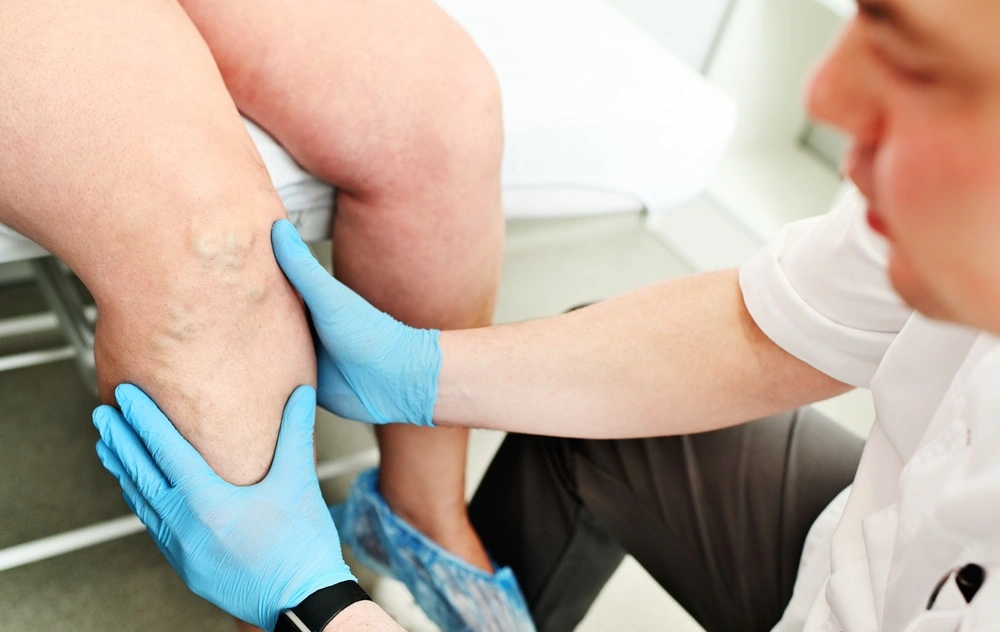
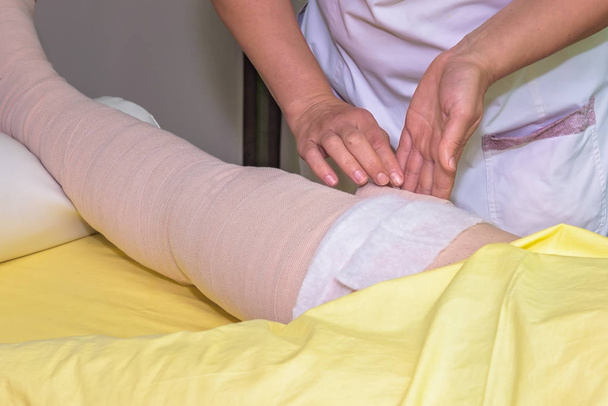
When to See a Doctor
If you experience persistent swelling in your arm or leg, it’s important to make an appointment with your doctor promptly. Don’t delay—reach out to your GP or call 111 as soon as possible.
For those already diagnosed with lymphoedema, a sudden or significant increase in limb size requires immediate medical attention to rule out potential complications and ensure effective management.
Raise Hand For Charity
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus.
